The 1776 to 1976 quarter dollar, often called the Bicentennial quarter, was minted to celebrate the 200th anniversary of American independence. While most of these coins remain common in circulation, certain versions—those with “D,” “S,” or no mint mark—can be worth more depending on their rarity, silver content, condition, and minting errors.
This article explores the value of Bicentennial quarters, the differences between mint marks, and what makes some of these coins valuable treasures.
Historical Background of the Bicentennial Quarter

The Bicentennial quarter was first issued in 1975 and 1976 with the special dual date “1776–1976”. Its reverse design features a drummer boy holding a military drum, created by Jack L. Ahr, symbolizing America’s spirit of independence.
Unlike standard Washington quarters, Bicentennial quarters were produced in massive quantities to commemorate the occasion. However, certain mint marks, special silver editions, and error coins have made some examples far more valuable than others.
1776 to 1976 Quarter Dollar Value Chart
| Mint Mark | Extremely Fine | MS63 | MS65 | MS67 | MS68 |
| 1776-1976 (P) No Mint Mark Quarter Dollar | $0.30 | $5 | $15 | $75 | $467 |
| 1776-1976 D Quarter Dollar | $0.30 | $5 | $15 | $70 | $7000 |
| 1776-1976 S Quarter Dollar | $3 | $5 | $12 to $218 | $30 to $352 | $85+ |
Understanding Mint Marks: “D,” “S,” and No Mint Mark
Mint marks on quarters tell us where they were minted:
- “D” Mint Mark – Denver Mint
- Found on coins minted in Denver.
- Typically made in copper-nickel clad.
- Circulated examples are usually worth face value, but high-grade MS coins or error pieces can be worth much more.
- “S” Mint Mark – San Francisco Mint
- Produced as proof coins, many in 40% silver compositions for collectors.
- Proof coins with mirror-like surfaces are more valuable, especially if graded PR-69 or PR-70.
- No Mint Mark – Philadelphia Mint
- Indicates the coin was minted in Philadelphia.
- Billions were produced, making them common, but pristine uncirculated examples or errors still hold significant value.
Values of 1776–1976 Bicentennial Quarters by Mint Mark
1. “D” Mint Bicentennial Quarter Value
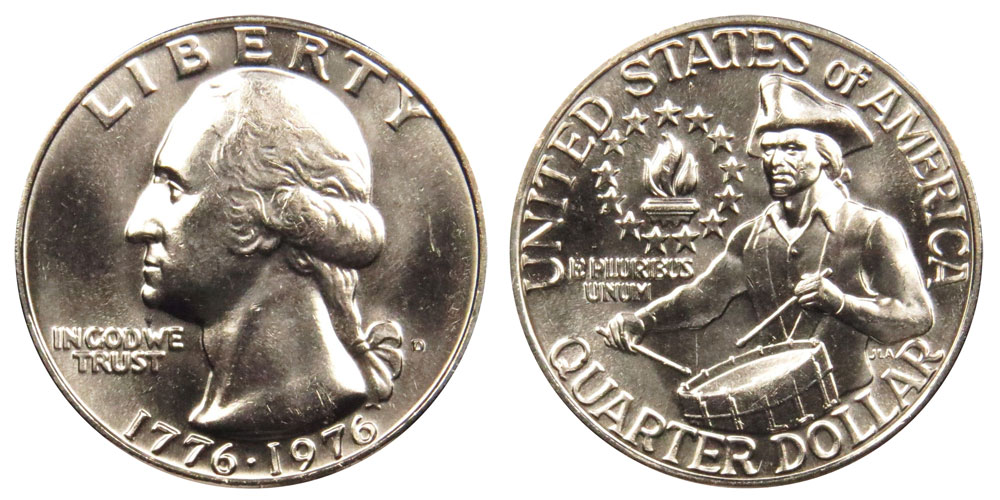

- Circulated: Face value (25 cents).
- MS-65: Around $5–$10.
- Higher grades (MS-67 or above): Can reach hundreds of dollars.
- Error coins: Off-center strikes, double dies, or wrong planchets may sell for thousands.
2. “S” Mint Bicentennial Quarter Value
- Clad Proof: $1–$3 in common condition.
- Silver Proof: $8–$15 in standard condition.
- PR-70 Silver Proofs: Can exceed hundreds or even thousands at auction.
3. No Mint Mark Bicentennial Quarter Value
- Circulated: Face value.
- MS-65: Around $5–$10.
- MS-67 and higher: $100+ depending on demand.
- Errors: Rare double dies and misstrikes can command large premiums.
Rare Errors and Varieties
Some Bicentennial quarters have become valuable due to minting mistakes. Examples include:
- Double Die Obverse/Reverse – Lettering or drummer boy appears doubled.
- Off-Center Strikes – Part of the design is missing due to misalignment.
- Wrong Planchet Errors – Quarters struck on dime or nickel blanks.
- Clipped Planchets – Portions of the coin’s edge are missing.
Error coins often sell for thousands, depending on rarity and condition.
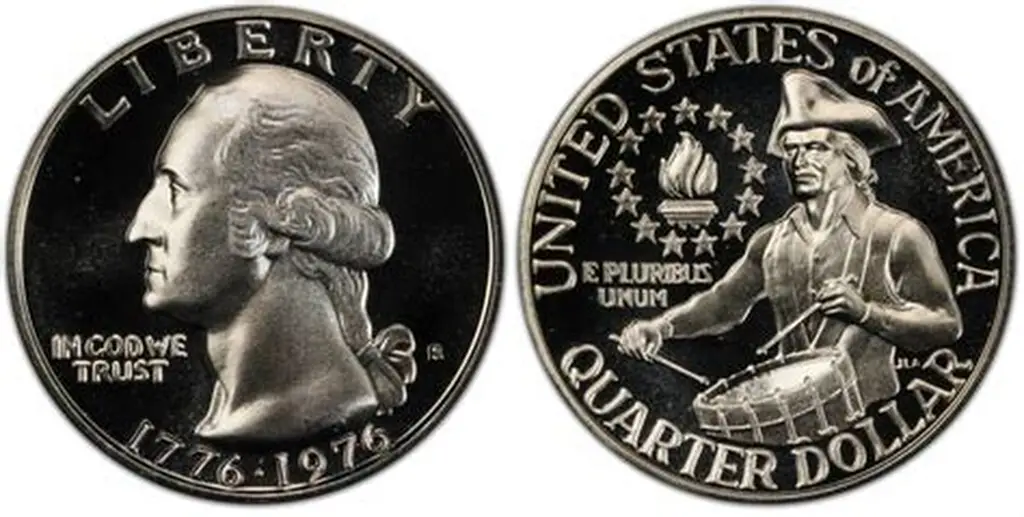
Silver Bicentennial Quarters
Not all Bicentennial quarters were made in copper-nickel. The San Francisco Mint struck 40% silver versions for collector sets.
- 40% Silver Uncirculated: Valued $5–$20.
- Silver Proofs: $8–$30 in typical condition.
- High-grade PR-70 Silver Proofs: Worth hundreds or thousands depending on rarity.
Silver content adds intrinsic value, making these coins more desirable to collectors and investors.

How to Tell If You Have a Valuable Bicentennial Quarter
- Check the Mint Mark – Located on the obverse, near Washington’s ponytail.
- Look for Silver – Silver versions weigh slightly more (5.75 g vs 5.67 g) and sound different when tapped.
- Inspect for Errors – Use magnification to spot doubled lettering, misstrikes, or planchet mistakes.
- Consider Condition – Higher-grade coins (MS-67 or PR-70) fetch far higher prices.
- Get Professional Grading – PCGS or NGC certification guarantees authenticity and boosts market value.
Where to Sell Valuable Bicentennial Quarters
If you own a rare or high-grade Bicentennial quarter, consider these selling avenues:
- Coin Shows and Dealers – Trusted way to connect with collectors.
- Online Auctions (eBay, Heritage Auctions, Stack’s Bowers) – Reach a wider audience of global buyers.
- Private Sales – High-value coins may be sold directly to collectors or investors.
Always ensure your coin is graded and authenticated before selling to maximize returns.
The Collector’s Appeal of Bicentennial Quarters
Bicentennial quarters remain among the most collected U.S. coins due to their patriotic design, historical context, and potential for rarity. Even ordinary versions are treasured keepsakes, while rare proofs, errors, and pristine examples have become serious investments.
Conclusion
The 1776 to 1976 Bicentennial quarter is an iconic piece of American history. While most are worth only face value, certain “D,” “S,” and no mint mark coins—especially silver proofs, errors, and high-grade examples—are worth significantly more.
Collectors should check their coins carefully, as one overlooked Bicentennial quarter could transform into a valuable numismatic treasure.
FAQs:
Are 1776–1976 “D” mint mark quarters valuable?
Most are face value, but high-grade MS examples or rare errors can reach hundreds, with exceptional coins selling for thousands.
What makes the 1776–1976 “S” mint quarters special?
San Francisco struck proof and 40% silver versions, with silver proofs and PR-70 grades commanding premium values among collectors.
Do 1776–1976 quarters without mint marks have value?
Philadelphia-issued coins are common, but pristine uncirculated MS-67 or error coins can fetch significant prices at auctions.
How can I identify a valuable Bicentennial quarter quickly?
Check mint mark, weight for silver content, search for minting errors, and consider professional grading for authentication and maximum value.
